Effective thermal management is essential to ensure the reliability and safety of power semiconductor devices, particularly under short-circuit stress in automotive applications. These advanced devices operate under dynamic conditions, experiencing rapid fluctuations in current and temperature during fault events. This makes precise thermal mapping indispensable, providing real-time insights into heat generation, hot spot evolution, and protection activation.
This is extremely useful because no simulator can provide reliable information about potential hot spots or unbalanced current paths across different channels.
These can create focal points leading to thermal drifts that trigger device shutdown protections, causing malfunctions or even failures.
Consequently, thermal validation requires detailed spatial and temporal temperature analysis beyond simple junction temperature measurements. For automotive intelligent multichannel drivers and smart fuses, robust thermal management ensures:
- Long-term durability
- Compliance with safety standards
- Overall system reliability
Why precise thermal mapping is important
For engineers, precise knowledge of thermal behavior is crucial for several reasons:
- Design optimization
It enables engineers to optimize system designs by identifying critical thermal stress points, ensuring components operate within safe temperature limits. - Reliability assurance
Understanding dynamic thermal behavior helps predict potential failure modes caused by overheating, improving device reliability and lifespan. - Protection strategy development
Insights into the timing and location of temperature peaks allow engineers to fine-tune protection mechanisms, preventing unnecessary shutdowns or catastrophic failures. - System integration
It supports accurate thermal modeling and validation in complex automotive systems, where multiple channels and components interact thermally. - Compliance and safety
Ensures that products meet stringent automotive safety standards by validating thermal performance under realistic fault conditions.
What most people know about
thermal validation
It’s about temperature - but the story goes deeper
While many focus on junction temperature limits, thermal validation involves much more: understanding the precise location of hot spots, how heat spreads across the die, and how the device’s protection mechanisms like thermal shutdown (TSD) respond dynamically.
The VNF9Q20F, part of our STi²Fuse series, is a 4-channel high-performance smart switch designed for demanding automotive applications, where robust thermal management is critical. To thoroughly characterize its thermal behavior and assess the effectiveness of intelligent protections in harsh automotive applications, the device is analyzed under challenging load short-circuit (LSC) conditions. These conditions arise when there is an inductive path between the load and the power source, leading to a sudden surge in current flow.

Test conditions considered:
Test conditions considered:
- Ambient temperature, Tamb = 25 °C
- DC battery voltage, Vbat = 13 V
- Short-circuit event duration :
- ton = 4 ms for mapping
- ton = 150 ms for temperature acquisition of both cold and hot thermal sensors and hot spots
- Load short-circuit (LSC) condition:
- Battery inductance, LSUPPLY = 5 µH
- Battery resistance, RSUPPLY = 10 mΩ
- Short-circuit inductance, LSHORT = 5 µH
- Short-circuit resistance, RSHORT = 100 mΩ
A high-resolution infrared sensor is used to capture a detailed 50x50 matrix of infrared emissions at each location, which are then converted into temperature values with a spatial resolution of approximately 30 μm.
This approach provides an unprecedented, fine-grained view of the device’s thermal profile during short-circuit pulses, enabling engineers to analyze temperature distribution and evolution with exceptional accuracy.
3 insights often overlooked before starting thermal validation
High spatial resolution is key to detecting critical hot spots. The VNF9Q20F’s thermal mapping scanned about 2500 points, enabling accurate identification of localized heating that could lead to failure if missed.
Thermal behavior is dynamic. By applying both short (5 ms) and extended (150 ms) pulses, the VNF9Q20F study tracked temperature changes over time at hot spots and thermal sensor locations. This analysis revealed the rapid heating characteristics of the device and the corresponding activation of protection mechanisms.
Understanding temperature evolution during short-circuit pulses is essential for customer engineers to optimize design, ensure reliability, and accurately implement protection strategies in automotive power devices.
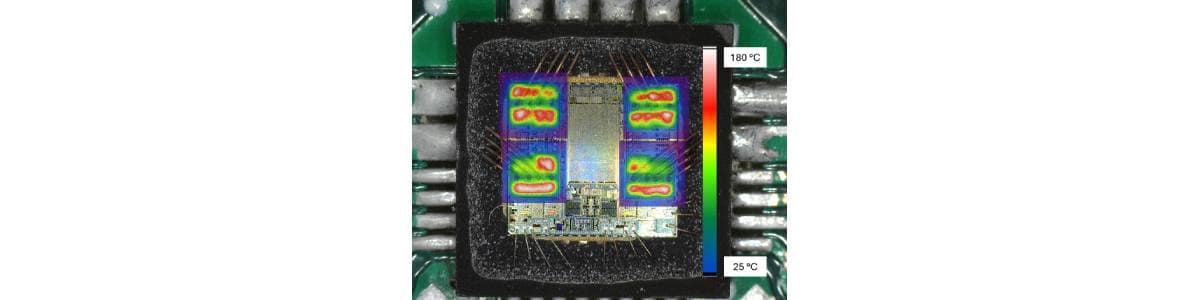
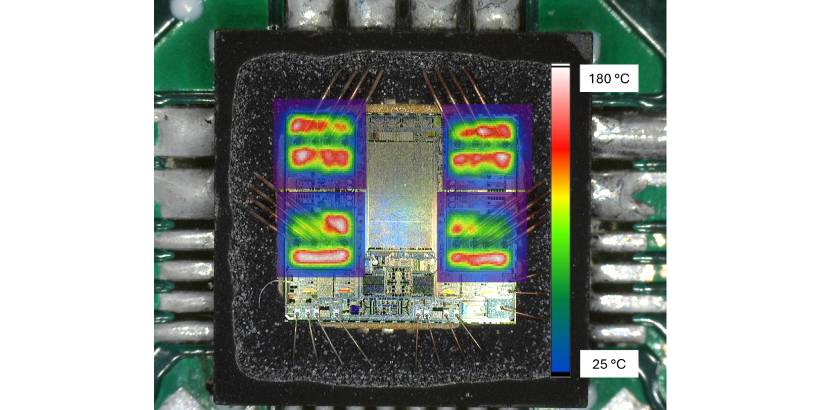
Emissivity variations, wire bonding, and surface conditions including molding residues can distort IR temperature measurements. Recognizing these influences is essential for accurate interpretation of thermal maps.



How to get started with effective
thermal validation
- Employ a high-resolution IR camera with fine spatial stepping (~30 μm).
- Capture dense temperature matrices during controlled short-circuit pulses.
- Analyze both spatial and temporal temperature data at key points.
- Consider packaging and surface effects on emissivity.
Design tips and insights for improved thermal performance

New design opportunities with STi2Fuse smart switches
New design opportunities with STi2Fuse smart switches
Webinar
Explore the features and benefits of ST's innovative STi2Fuse smart switches and discover how to integrate them into your next generation of protected and efficient circuit designs.

Key strategies for EMI compliance in intelligent power switches
Key strategies for EMI compliance in intelligent power switches
Whitepaper
Learn essential design tips and technical strategies to effectively manage electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure regulatory compliance in your power switch designs.